Introduction to Vegan Nutrition Guide
- What is veganism?
- Importance of nutrition in vegan lifestyle.
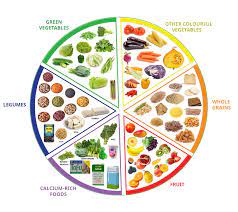
Key Nutrients in a Vegan Diet
- Protein
- Iron
- Calcium
- Vitamin B12
- Omega-3 fatty acids
Planning a Balanced Vegan Diet
- Whole grains and cereals
- Legumes and pulses
- Fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
Vegan Protein Sources
- Tofu and tempeh
- Lentils and beans
- Quinoa
- Seitan
Iron-Rich Foods for Vegans
- Spinach and kale
- Lentils and chickpeas
- Fortified cereals
Calcium Sources in Vegan Diet
- Fortified plant-based milk
- Leafy greens
- Almonds and sesame seeds
Importance of Vitamin B12 Supplementation
- Risks of deficiency
- Vegan-friendly B12 supplements
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Vegans
- Flaxseeds and chia seeds
- Walnuts
- Algal oil supplements
Tips for a Healthy Vegan Lifestyle
- Stay hydrated
- Include variety in meals
- Read labels carefully
- Consider consulting a nutritionist
Vegan Nutrition for Different Age Groups
- Children
- Teens
- Adults
- Seniors
Benefits of Vegan Nutrition
- Improved heart health
- Lower risk of certain cancers
- Sustainable and eco-friendly
Addressing Common Concerns About Vegan Nutrition
- Protein deficiency
- Iron deficiency
- Calcium deficiency
Transitioning to a Vegan Diet
- Gradual approach
- Seek support from vegan communities
Meal Planning and Recipes
- Sample meal plans
- Quick and easy vegan recipes
Conclusion
- Recap the importance of a balanced vegan diet
- Encourage further exploration of vegan nutrition
Vegan Nutrition Guide: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction to Vegan Nutrition
In recent years, veganism has gained significant popularity worldwide, not just as a dietary choice but as a lifestyle. Embracing a vegan lifestyle involves abstaining from the consumption of animal products and adopting a plant-based diet. However, with this transition comes the need for careful consideration of nutrition to ensure optimal health and wellbeing.
Key Nutrients in a Vegan Diet
Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient necessary for various bodily functions, including muscle repair and growth. Contrary to popular belief, sufficient protein intake is easily achievable on a vegan diet through plant-based sources such as legumes, tofu, and tempeh.
Iron
Iron assumes a critical part in the transportation of oxygen all through the body. While animal products are rich sources of iron, vegans can obtain this nutrient from plant-based sources like spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals.
Calcium
Calcium is fundamental for keeping up areas of strength for with and teeth. Vegan-friendly sources of calcium include fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens like kale and collard greens, as well as almonds and sesame seeds.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is basically found in creature items, making supplementation critical for vegetarians. B12 plays a vital role in nerve function and the production of red blood cells.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 unsaturated fats are fundamental for cerebrum wellbeing and diminishing irritation. Vegan sources of omega-3s include flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algal oil supplements.
Planning a Balanced Vegan Diet
Achieving a balanced vegan diet involves incorporating a variety of plant-based foods to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients.
Whole grains and cereals
Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, providing sustained energy throughout the day.
Legumes and pulses
Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and iron, making them essential components of a vegan diet.
Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, promoting overall health and wellbeing. Aim for a colorful variety to maximize nutrient intake.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are nutrient-dense foods rich in healthy fats, protein, and essential minerals. Incorporate them into meals, snacks, or as toppings for added nutrition.
Vegan Protein Sources
Tofu and tempeh
Tofu and tempeh are versatile plant-based protein sources that can be used in a variety of dishes, from stir-fries to sandwiches.
Lentils and beans
Lentils and beans are affordable and nutrient-rich, providing a significant amount of protein, fiber, and iron per serving.
Quinoa
Quinoa is a complete protein source, containing all nine essential amino acids, making it an excellent choice for vegans looking to increase their protein intake.
Seitan
Seitan, also known as wheat gluten, is a high-protein meat substitute commonly used in vegan cooking for its texture and flavor.
Iron-Rich Foods for Vegans
Spinach and kale
Dark leafy greens like spinach and kale are excellent sources of iron and other essential nutrients, such as vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption.
Lentils and chickpeas
Legumes like lentils and chickpeas are not only rich in iron but also provide a substantial amount of protein and fiber, making them a staple in vegan diets.
Fortified cereals
Many breakfast cereals are fortified with iron, making them a convenient and accessible source of this essential nutrient for vegans.
Calcium Sources in Vegan Diet
Fortified plant-based milk
Fortified plant-based milk alternatives like soy milk, almond milk, and oat milk are excellent sources of calcium, often containing as much or more calcium than dairy milk.
Leafy greens
Leafy green vegetables such as bok choy, collard greens, and broccoli are naturally rich in calcium and can be easily incorporated into various dishes.
Almonds and sesame seeds
Nuts and seeds like almonds and sesame seeds are not only delicious but also provide a significant amount of calcium, making them valuable additions to a vegan diet.
Importance of Vitamin B12 Supplementation
Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell production, yet it is primarily found in animal products. Therefore, vegans must supplement their diet with B12 to prevent deficiency and maintain optimal health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Vegans
Omega-3 unsaturated fats are fundamental for cerebrum wellbeing and decreasing irritation. While fatty fish is a traditional source of omega-3s, vegans can obtain these essential fats from plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algal oil supplements.
Tips for a Healthy Vegan Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy vegan lifestyle goes beyond just dietary choices. Here are some tips to ensure you thrive on a plant-based diet:
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Incorporate an assortment of plant-based food varieties in your eating regimen to guarantee you get a great many supplements.
Read labels carefully to avoid hidden animal-derived ingredients in packaged foods.
Consider consulting a nutritionist or dietitian for personalized guidance and advice.
Vegan Nutrition for Different Age Groups
Children
A well-planned vegan diet can meet the nutritional needs of children, but extra attention should be paid to ensuring they get enough protein, calcium, iron, and vitamin B12 for growth and development.
Teens
Teenagers may have increased energy and nutrient needs due to growth spurts. Encourage them to eat a variety of plant-based foods to meet their nutritional requirements for optimal health.
Adults
Adults can thrive on a vegan diet with proper planning and attention to nutrient intake. Focus on incorporating a variety of whole foods to ensure adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Seniors
As we age, our nutritional needs may change. Seniors should pay attention to calcium and vitamin D intake for bone health and consider B12 supplementation to prevent deficiency.
Benefits of Vegan Nutrition
Beyond individual health, vegan nutrition offers various benefits for both the environment and animals:
Further developed heart wellbeing because of lower admission of immersed fats and cholesterol.
Reduced risk of certain cancers, such as colorectal cancer, linked to high consumption of red and processed meats.
Environmental sustainability, as plant-based diets have a lower carbon footprint compared to animal agriculture.
Addressing Common Concerns About Vegan Nutrition
Despite its numerous health benefits, vegan nutrition may raise concerns regarding potential nutrient deficiencies. This is the way to address a few normal worries:
Protein deficiency can be avoided by consuming a variety of plant-based protein sources such as legumes, tofu, and quinoa.
Iron deficiency can be prevented by incorporating iron-rich plant foods like leafy greens, lentils, and fortified cereals into your diet.
Calcium deficiency can be mitigated by consuming fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, and calcium-rich nuts and seeds.
Transitioning to a Vegan Diet
Changing to a vegetarian diet can be a progressive interaction. Start by incorporating more plant-based meals into your routine and gradually phasing out animal products. Seek support from vegan communities, online resources, and cookbooks to make the transition smoother and more enjoyable.
Meal Planning and Recipes
Planning meals as a vegan doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some simple meal ideas and recipes to inspire your plant-based journey:
Breakfast: Overnight oats topped with fresh fruit and nuts
Lunch: Quinoa salad with simmered vegetables and chickpeas
Supper: Pan-seared tofu with blended vegetables and earthy colored rice
Snacks: Hummus with carrot sticks, fruit smoothies, or mixed nuts
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-planned vegan diet can provide all the essential nutrients your body needs for optimal health and wellbeing. By focusing on a variety of whole, plant-based foods, you can enjoy the numerous benefits of vegan nutrition while contributing to a more sustainable and compassionate world.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is it conceivable to get sufficient protein on a veggie lover diet?
Yes, it is entirely possible to meet your protein needs on a vegan diet by consuming a variety of plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, and tempeh.
How can vegans ensure they get enough calcium without dairy products?
Vegans can obtain calcium from fortified plant-based milk, leafy greens, almonds, and sesame seeds.
Do vegans need to take supplements?
Vitamin B12 supplementation is recommended for vegans to prevent deficiency, as this nutrient is primarily found in animal products.
Are there any wellbeing chances related with a vegetarian diet?
With proper planning, a vegan diet can be healthy and nutritionally adequate for all stages of life. However, it’s essential to pay attention to nutrient intake to prevent deficiencies.
Can children follow a vegan diet?
Yes, children can thrive on a well-planned vegan diet with attention to essential nutrients like protein, calcium, iron, and vitamin B12. Consultation with a healthcare professional or dietitian is recommended to ensure nutritional needs are met during growth and development.

2 thoughts on “Unleash the Power of Plants: A Comprehensive Vegan Nutrition Guide for 2024!”