Introduction to Autotrophic Nutrition
- Explanation of autotrophic nutrition.
- Importance of understanding autotrophic nutrition.
What Plants Teach Us About Sustainable Eating
- Overview of sustainable eating habits.
- Role of plants in sustainable eating.
Efficiency of Autotrophic Nutrition
- How plants efficiently produce their own food.
- Lessons for sustainable food production.
Reducing Environmental Impact
- Comparison between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition.
- Impact on the environment.
Nutritional Value of Plants
- Diversity of nutrients in plant-based foods.
- Health benefits of consuming plants.
Plant-Based Diets for Health and Sustainability
- Link between plant-based diets and health.
- Environmental benefits of plant-based diets.
Challenges and Solutions
- Challenges faced in adopting plant-based diets.
- Solutions to overcome these challenges.
Educational Initiatives
- Importance of educating people about autotrophic nutrition.
- Strategies for promoting plant-based eating habits.
Case Studies and Examples
- Examples of successful initiatives promoting plant-based diets.
- Impact on communities and the environment.
Cultural Perspectives
- Cultural influences on dietary habits.
- Integration of plant-based foods into various cuisines.
Future Trends
- Emerging trends in sustainable eating.
- Innovations in plant-based food production.
Conclusion
- Recap of key points.
- Importance of adopting sustainable eating habits inspired by autotrophic nutrition.
FAQs
- What is autotrophic nutrition?
- How can plant-based diets benefit the environment?
- Are there any drawbacks to plant-based diets?
- How can individuals transition to a plant-based diet?
- What are some common misconceptions about plant-based eating?
Introduction to Autotrophic Nutrition
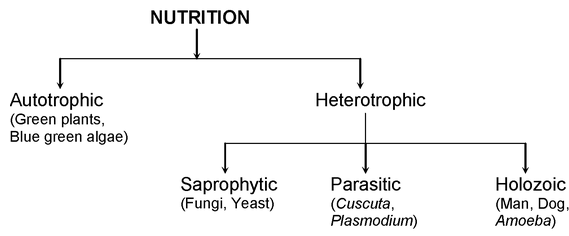
Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms, primarily plants, produce their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. This self-sustaining mechanism is fundamental to the survival of plants and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding autotrophic nutrition is essential as it provides insights into sustainable eating habits. By examining how plants efficiently produce their own food, we can learn valuable lessons for sustainable food production and consumption.
Table of Contents
What Plants Teach Us About Sustainable Eating
In today’s world, where concerns about environmental sustainability are paramount, plants offer valuable lessons in sustainable eating. Sustainable eating habits involve consuming foods that have minimal impact on the environment, promote biodiversity, and support long-term ecological balance.
Plants play a central role in sustainable eating for several reasons. Firstly, they require fewer resources such as land, water, and energy compared to animal agriculture. By relying on plants as a primary source of nutrition, we can reduce the strain on natural resources and mitigate environmental degradation.
Efficiency of Autotrophic Nutrition
Plants possess remarkable efficiency in converting sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. This ability to harness solar energy and convert it into usable forms of food highlights the potential for sustainable food production.
By mimicking the efficiency of autotrophic nutrition, agricultural practices can become more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Innovations such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and agroforestry demonstrate how we can optimize food production while minimizing environmental impact.
Reducing Environmental Impact
Comparing autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition reveals significant differences in environmental impact. Autotrophic organisms, such as plants, produce their own food using sunlight, whereas heterotrophic organisms rely on consuming other organisms for nutrition.
The inefficiency of heterotrophic nutrition contributes to environmental degradation through deforestation, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, autotrophic nutrition minimizes these negative impacts by reducing the need for intensive land use and resource exploitation.
Nutritional Value of Plants
Plant-based foods are rich in essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that are vital for human health. A diet centered around fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes can provide all the necessary nutrients for optimal health and well-being.
Furthermore, research has shown that plant-based diets are associated with lower rates of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By prioritizing plant-based foods in our diet, we can improve our health while also reducing our environmental footprint.
Plant-Based Diets for Health and Sustainability
The shift towards plant-based diets is gaining momentum as people become more aware of the health and environmental benefits. Plant-based diets not only promote personal health but also contribute to the sustainability of our planet by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving natural resources.
Moreover, plant-based diets are inclusive and accessible to people of all socioeconomic backgrounds. By promoting plant-based eating habits, we can address issues of food insecurity, promote social justice, and build more resilient communities.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite the numerous benefits of plant-based diets, there are challenges associated with transitioning to a plant-based lifestyle. These challenges may include cultural barriers, lack of access to affordable plant-based foods, and misinformation about nutrition.
However, these challenges can be overcome through education, advocacy, and policy interventions. By raising awareness about the benefits of plant-based diets and providing support for individuals and communities, we can facilitate the transition to a more sustainable and compassionate way of eating.
Educational Initiatives
Educational initiatives play a crucial role in promoting plant-based eating habits and raising awareness about the importance of autotrophic nutrition. By integrating nutrition education into school curricula, promoting community gardens, and providing cooking classes, we can empower people to make informed dietary choices.
Furthermore, initiatives such as Meatless Mondays and Veganuary encourage individuals to explore plant-based eating and discover delicious alternatives to animal products. By harnessing the power of social media and grassroots activism, we can inspire a global movement towards sustainable eating.
Case Studies and Examples
Numerous case studies and examples demonstrate the effectiveness of plant-based diets in promoting health and sustainability. For instance, the Blue Zones, regions of the world known for longevity and vitality, have diets rich in plant-based foods and low in animal products.
Similarly, initiatives such as the Green Revolution in India have demonstrated the potential for sustainable agriculture to alleviate hunger and poverty while preserving natural resources. By studying these examples, we can learn valuable lessons for creating a more sustainable food system.
Cultural Perspectives
Cultural perspectives play a significant role in shaping dietary habits and food choices. Integrating plant-based foods into traditional cuisines can help bridge cultural divides and promote culinary diversity.
Moreover, cultural celebrations and festivals often revolve around food, providing opportunities to showcase plant-based alternatives and educate communities about sustainable eating practices. By celebrating the diversity of plant-based foods, we can create a more inclusive and sustainable food culture.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the future of sustainable eating holds promise as innovations in food technology and agricultural practices continue to emerge. From plant-based meat substitutes to lab-grown proteins, advancements in food science offer exciting possibilities for creating a more sustainable and ethical food system.
Furthermore, as consumer demand for plant-based products grows, businesses and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the economic and environmental benefits of investing in sustainable food production. By aligning incentives and promoting collaboration across sectors, we can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable food system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, autotrophic nutrition offers valuable insights into sustainable eating habits by highlighting the efficiency and resilience of plants as food producers. By learning from nature and adopting plant-based diets, we can promote personal health, environmental sustainability, and social justice.
By embracing plant-based eating habits and supporting initiatives that promote sustainable food production, we can create a brighter future for ourselves and future generations.
FAQs
What is autotrophic nutrition?
Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms, primarily plants, produce their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.How can plant-based diets benefit the environment?
Plant-based diets require fewer resources and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to diets high in animal products, making them more environmentally sustainable.Are there any drawbacks to plant-based diets?
While plant-based diets offer numerous health and environmental benefits, some individuals may face challenges in obtaining adequate nutrients or adjusting to a new way of eating.How can individuals transition to a plant-based diet?
Individuals can gradually transition to a plant-based diet by incorporating more fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes into their meals and experimenting with new recipes and flavors.What are some common misconceptions about plant-based eating?
Common misconceptions about plant-based eating include concerns about protein deficiency, taste, and affordability. However, with proper planning and education, these misconceptions can be debunked.

